0445 - Add two Numbers II (Medium)
Problem Link
https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers-ii/
Problem Statement
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The most significant digit comes first and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list. You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
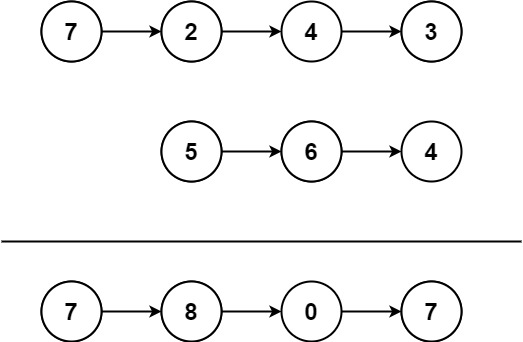
Input: l1 = [7,2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
Output: [7,8,0,7]
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
Output: [8,0,7]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
Output: [0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
Follow up:
Could you solve it without reversing the input lists?
Approach 1: Recursion
First, we will add zeros to the start of the smaller linked list such that both the lists become of equal size and then we will use recursion to perform and addition start to end.
For example -
After Adding zeros to the smaller linked list
Now, we will use recursion (like reverse traversal) to the end of both the lists and start addition from the end. After each recursion ends, and will be at their last nodes. We will add the both node values and pass from current recursive function to the previous recursive function, and each recursive call add the sum along with carry from the last previous call and builds the nodes in a reverse order.
For the above example, We traversed both linked list nodes till end of the list and added sum, passing the result to previous call.
, and new_node -> val = sum%10, and = sum/10
, and new_node -> val = , and recursive function will return with (last node of final linked list). , and new_node -> val = , and recursive function will return with , , and new_node -> val = , and recursive function will return with , , and new_node -> val = , and recursive function will return with (Head node of final linked list)
Finally, our result will be
Time Complexity is , where is the length of longest linked list.
Space Complexity is , where is the recursive call stack of the linked list.
- C++
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode * next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode * next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode * addDigits (ListNode * l1, ListNode * l2, int &carry) {
// First, we will check if our both linked list's node is NULL or not
if (l1 == NULL && l2 == NULL)
return NULL;
// Creating new_node for store the sum of digits
ListNode * new_node = new ListNode(-1);
// Here, we are making link between nodes which are having the sum of digits
new_node -> next = addDigits(l1 -> next, l2 -> next, carry);
// Sum up both node values and assign the current node
new_node -> val = (l1 -> val + l2 -> val + carry) % 10;
// Calculate carry if the current sum > 9
carry = (l1 -> val + l2 -> val + carry) / 10;
return new_node;
}
ListNode * addTwoNumbers (ListNode * l1, ListNode * l2) {
// Adding zeros to the start of the smaller list:
ListNode * first = l1, * second = l2;
while (first != NULL || second != NULL) {
// Add leading zero's to the nodes to the one is smaller, till both nodes length becomes equal
if (first == NULL) {
// Create new node ( value of new node is 0
ListNode * new_node = new ListNode(0);
// Connecting new node to head of linkedlist l1
new_node -> next = l1;
// Now, we assign new_node as head of linked list l1
l1 = new_node;
second = second -> next;
} else if (second == NULL) {
ListNode * new_node = new ListNode(0);
new_node -> next = l2;
l2 = new_node;
first = first -> next;
} else {
first = first -> next;
second = second -> next;
}
}
int carry = 0;
// Create a new node temp (Head of the linked list) for sum of two linked list's l1 and l2
ListNode * temp = new ListNode(-1);
// Call recursion function for traversing of the linked list and Calculating the sum of digits
temp -> next = addDigits(l1, l2, carry);
// If carry is remaining, then add it to the last node (will be the Head)
if (carry != 0) {
ListNode * new_node = new ListNode(carry);
new_node -> next = temp -> next;
temp -> next = new_node;
}
return temp -> next;
}
};
Approach 2: Stack
Numbers are stored forward order, so keep traversing the nodes and add it to the stack. Now at the last, the last node will be at top of the stack. Pop top of the stack one by one and add the digits and create a node and keep the last node for the next node pointer (same as Reverse LinkedList). In each iteration, the current node will be set to prev node next pointer. Finally if carry is remaining then add it to head.
Time Complexity is , where is the length of longest linked list.
Space Complexity is
- Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<>();
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
if (l1 != null) {
s1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l2 != null) {
s2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
ListNode head = new ListNode();
ListNode current = null, prev = null;
int carry = 0;
while (!s1.isEmpty() || !s2.isEmpty()) {
int sum = carry;
if (!s1.isEmpty()) sum += s1.pop().intValue();
if (!s2.isEmpty()) sum += s2.pop().intValue();
carry = sum / 10;
current = new ListNode(sum % 10);
// Set current node next pointer to prev node
current.next = prev;
// Head is point to current and last previous node
head.next = current;
prev = current;
}
if (carry == 1) {
current = new ListNode(carry);
current.next = prev;
head.next = current;
}
return head.next;
}
}