1305 - All Elements in Two Binary Search Trees (Medium)
Problem Link
https://leetcode.com/problems/all-elements-in-two-binary-search-trees/
Problem Statement
Given two binary search trees root1 and root2, return a list containing all the integers from both trees sorted in ascending order.
Example 1:
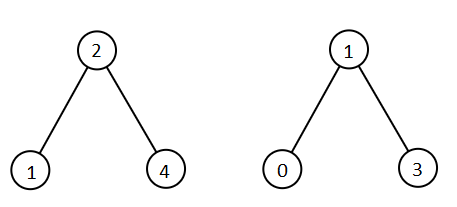
Input: root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3]
Output: [0,1,1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
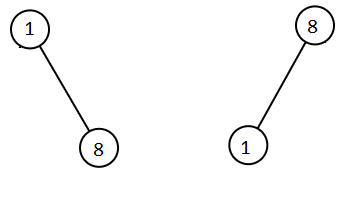
Input: root1 = [1,null,8], root2 = [8,1]
Output: [1,1,8,8]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Prerequisite
Approach 1: DFS Traversal and Sorting
In this problem, we can use either one to traverse all nodes and put them into a common array. We sort the array at the end.
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> s;
void dfs(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return;
dfs(node->left);
s.push_back(node->val);
dfs(node->right);
}
vector<int> getAllElements(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
dfs(root1);
dfs(root2);
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
return s;
}
};
However, we can see the in-order traversal is faster than the other two. This is because the array is already sorted after the traversal for binary tree. In example 1, after the traversal, we will have [1, 2, 4] and [0, 1, 3].
| Traversal | Runtime | Memory | Language |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-order | 309 ms | 85.4 MB | cpp |
| In-order | 132 ms | 85.3 MB | cpp |
| Post-order | 211 ms | 85.4 MB | cpp |
Approach 2: In-order Traversal + Merging
As we know In-order traversal will make the array sorted, the remaining problem is same as "merging two sorted arrays into one".
class Solution {
public:
void inorder(TreeNode* node, vector<int>& res) {
if (node == NULL) return;
inorder(node->left, res);
res.push_back(node->val);
inorder(node->right, res);
}
vector<int> merge(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b) {
vector<int> res;
int n = (int) a.size(), m = (int) b.size();
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m) {
if (a[i] < b[j]) res.push_back(a[i++]);
else res.push_back(b[j++]);
}
while (i < n) res.push_back(a[i++]);
while (j < m) res.push_back(b[j++]);
return res;
}
vector<int> getAllElements(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
vector<int> a, b;
inorder(root1, a); inorder(root2, b);
return merge(a, b);
}
};