2359 - Find Closest Node to Given Two Nodes (Medium)
Problem Link
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-closest-node-to-given-two-nodes
Problem Statement
You are given a directed graph of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1, where each node has at most one outgoing edge.
The graph is represented with a given 0-indexed array edges of size n, indicating that there is a directed edge from node i to node edges[i]. If there is no outgoing edge from i, then edges[i] == -1.
You are also given two integers node1 and node2.
Return the index of the node that can be reached from both node1 and node2, such that the maximum between the distance from node1 to that node, and from node2 to that node is minimized. If there are multiple answers, return the node with the smallest index, and if no possible answer exists, return -1.
Note that edges may contain cycles.
Example 1:
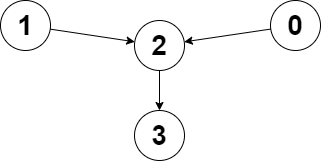
Input: edges = [2,2,3,-1], node1 = 0, node2 = 1
Output: 2
Explanation: The distance from node 0 to node 2 is 1, and the distance from node 1 to node 2 is 1.
The maximum of those two distances is 1. It can be proven that we cannot get a node with a smaller maximum distance than 1, so we return node 2.
Example 2:
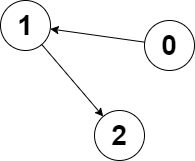
Input: edges = [1,2,-1], node1 = 0, node2 = 2
Output: 2
Explanation: The distance from node 0 to node 2 is 2, and the distance from node 2 to itself is 0.
The maximum of those two distances is 2. It can be proven that we cannot get a node with a smaller maximum distance than 2, so we return node 2.
Constraints:
n == edges.length2 <= n <= 10^5-1 <= edges[i] < nedges[i] != i0 <= node1, node2 < n
Approach 1: DFS x 2
Since there is only at most 1 outgoing edge, we can simply use DFS.
- C++
- Java
- Python
- Rust
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(int u, vector<int>& d, vector<int>& vis, vector<int>& edges) {
// mark it visited
vis[u] = 1;
// check the outgoing edge
int v = edges[u];
// -1 means there is no outgoing edge, so we skip it
// if it is visited, we also skip it
if (v != -1 && !vis[v]) {
// the dist going to node v form node u is simply d[u] + 1
d[v] = d[u] + 1;
// dfs on neigbour node `v`
dfs(v, d, vis, edges);
}
}
int closestMeetingNode(vector<int>& edges, int node1, int node2) {
int n = edges.size();
// d1[i]: shortest dist to node i starting from node 1
// d2[i]: shortest dist to nodes i starting from node 2
vector<int> d1(n, INT_MAX), d2(n, INT_MAX);
// vis1[i]: true if node i is visited else false. used for building d1
// vis2[i]: true if node i is visited else false. used for building d2
vector<int> vis1(n, 0), vis2(n, 0);
// dist to node1 from node1 is 0, same as node2
d1[node1] = 0, d2[node2] = 0;
// build the dist for d1
dfs(node1, d1, vis1, edges);
// build the dist for d2
dfs(node2, d2, vis2, edges);
// iterate each node to find the min max dist
int ans = -1, mi = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (max(d1[i], d2[i]) < mi) {
mi = max(d1[i], d2[i]);
ans = i;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
class Solution {
public void dfs(int u, int[] d, boolean[] vis, int[] edges) {
// mark it visited
vis[u] = true;
// check the outgoing edge
int v = edges[u];
// -1 means there is no outgoing edge, so we skip it
if (v != -1 && !vis[v]) {
// the dist going to node v form node u is simply d[u] + 1
d[v] = d[u] + 1;
// dfs on neigbour node `v`
dfs(v, d, vis, edges);
}
}
public int closestMeetingNode(int[] edges, int node1, int node2) {
int n = edges.length;
// d1[i]: shortest dist to node i starting from node 1
// d2[i]: shortest dist to nodes i starting from node 2
int[] d1 = new int[n];
int[] d2 = new int[n];
// vis1[i]: true if node i is visited else false. used for building d1
// vis2[i]: true if node i is visited else false. used for building d2
boolean[] vis1 = new boolean[n];
boolean[] vis2 = new boolean[n];
Arrays.fill(d1, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Arrays.fill(d2, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// dist to node1 from node1 is 0, same as node2
d1[node1] = d2[node2] = 0;
// build the dist for d1
dfs(node1, d1, vis1, edges);
// build the dist for d2
dfs(node2, d2, vis2, edges);
// iterate each node to find the min max dist
int ans = -1, mi = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (Math.max(d1[i], d2[i]) < mi) {
mi = Math.max(d1[i], d2[i]);
ans = i;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
class Solution:
def closestMeetingNode(self, edges: List[int], node1: int, node2: int) -> int:
def dfs(u: int, d: List[int], vis: List[bool], edges: List[int]) -> None:
# mark it visited
vis[u] = True
# check the outgoing edge
v = edges[u]
# -1 means there is no outgoing edge, so we skip it
# if it is visited, we also skip it
if v != -1 and not vis[v]:
# the dist going to node v form node u is simply d[u] + 1
d[v] = d[u] + 1
# dfs on neigbour node `v`
dfs(v, d, vis, edges)
n = len(edges)
# d1[i]: shortest dist to node i starting from node 1
# d2[i]: shortest dist to nodes i starting from node 2
d1, d2 = [float("inf")] * n, [float("inf")] * n
# vis1[i]: true if node i is visited else false. used for building d1
# vis2[i]: true if node i is visited else false. used for building d2
vis1, vis2 = [False] * n, [False] * n
# dist to node1 from node1 is 0, same as node2
d1[node1], d2[node2] = 0, 0
# build the dist for d1
dfs(node1, d1, vis1, edges)
# build the dist for d2
dfs(node2, d2, vis2, edges)
# iterate each node to find the min max dist
ans = -1
mi = float("inf")
for i in range(n):
if max(d1[i], d2[i]) < mi:
mi = max(d1[i], d2[i])
ans = i
return ans
use std::cmp::max;
impl Solution {
fn dfs(u: i32, d: &mut Vec<i32>, vis: &mut Vec<bool>, edges: &Vec<i32>) {
// mark it visited
vis[u as usize] = true;
// check the outgoing edge
let v = edges[u as usize];
// -1 means there is no outgoing edge, so we skip it
// if it is visited, we also skip it
if v != -1 && !vis[v as usize] {
// the dist going to node v form node u is simply d[u] + 1
d[v as usize] = d[u as usize] + 1;
// dfs on neigbour node `v`
Self::dfs(v, d, vis, edges);
}
}
pub fn closest_meeting_node(edges: Vec<i32>, node1: i32, node2: i32) -> i32 {
let n = edges.len();
// d1[i]: shortest dist to node i starting from node 1
// d2[i]: shortest dist to nodes i starting from node 2
let mut d1 = vec![i32::MAX; n];
let mut d2 = vec![i32::MAX; n];
// vis1[i]: true if node i is visited else false. used for building d1
// vis2[i]: true if node i is visited else false. used for building d2
let mut vis1 = vec![false; n];
let mut vis2 = vec![false; n];
// dist to node1 from node1 is 0, same as node2
d1[node1 as usize] = 0;
d2[node2 as usize] = 0;
// build the dist for d1
Self::dfs(node1, &mut d1, &mut vis1, &edges);
// build the dist for d2
Self::dfs(node2, &mut d2, &mut vis2, &edges);
// iterate each node to find the min max dist
let mut ans = -1;
let mut mi = i32::MAX;
for i in 0..n {
if max(d1[i], d2[i]) < mi {
mi = max(d1[i], d2[i]);
ans = i as i32;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Approach: Dijkstra x 2
Dijkstra approach in this question is not recommended but here's how we do in case there are multiple outgoing edges.
- C++
class Solution {
public:
// https://leetcodethehardway.com/tutorials/graph-theory/dijkstra
template<typename T_pair, typename T_vector>
void dijkstra(T_pair &g, T_vector &dist, int start) {
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> pq;
dist[start] = 0;
pq.push({start, 0});
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto [u_node, u_cost] = pq.top(); pq.pop();
if (u_cost > dist[u_node]) continue;
for (auto [v_node, v_cost] : g[u_node]) {
if (dist[v_node] > dist[u_node] + v_cost) {
dist[v_node] = dist[u_node] + v_cost;
pq.push({v_node, dist[v_node]});
}
}
}
}
int closestMeetingNode(vector<int>& edges, int node1, int node2) {
int n = edges.size();
// d1[i]: shortest dist to node i starting from node 1
// d2[i]: shortest dist to nodes i starting from node 2
vector<int> d1(n, INT_MAX), d2(n, INT_MAX);
// build the graph
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> g(n);
// iterate each node
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// if there is outgoing edge from node i
if (edges[i] != -1) {
// by default, we define the dist to edges[i] is 1
g[i].push_back({edges[i], 1});
}
}
// build the dist for d1
dijkstra(g, d1, node1);
// build the dist for d2
dijkstra(g, d2, node2);
// iterate each node to find the min max dist
int ans = -1, mi = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (max(d1[i], d2[i]) < mi) {
mi = max(d1[i], d2[i]);
ans = i;
}
}
return ans;
}
};