0941 - Valid Mountain Array (Easy)
Problem Link
https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-mountain-array/
Problem Statement
Given an array of integers arr, return true if and only if it is a valid mountain array.
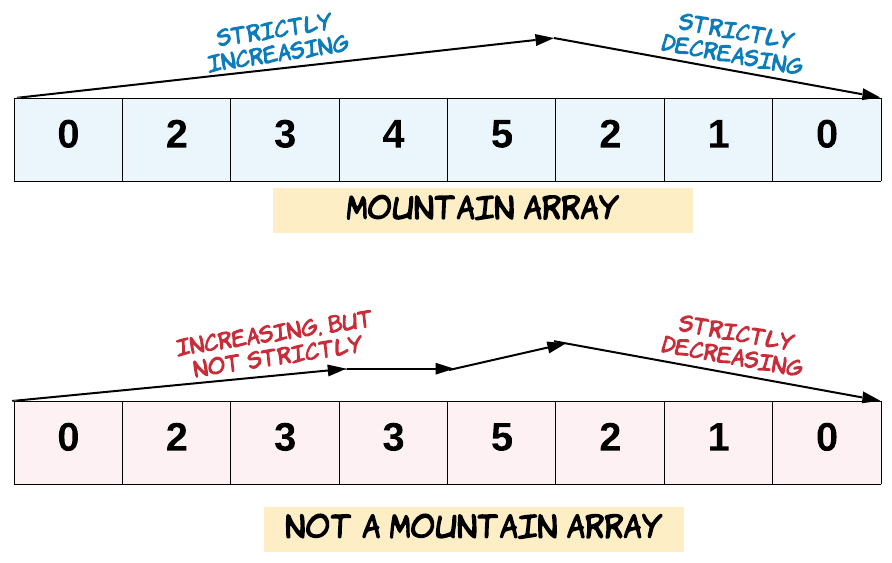
Recall that arr is a mountain array if and only if:
arr.length >= 3- There exists some
iwith0 < i < arr.length - 1such that:arr[0] < arr[1] < ... < arr[i - 1] < arr[i]arr[i] > arr[i + 1] > ... > arr[arr.length - 1]
Example 1:
Input: arr = [2,1]
Output: false
Example 2:
Input: arr = [3,5,5]
Output: false
Example 3:
Input: arr = [0,3,2,1]
Output: true
Constraints:
1 <= arr.length <= 10^40 <= arr[i] <= 10^4
Approach 1: Prefix and Suffix
If the array length is less than 3, then it must be false. Otherwise, we can calculate the prefix and suffix. prefix[i] means it is a strictly increasing array from the first mountain till mountain i. Similarly, suffix[j] means it is a strictly decreasing array from the last mountain till mountain j. If there is a certain point k where prefix[k] and suffix[k] both true, then that would be the peak of a valid mountain.
- C++
class Solution {
public:
bool validMountainArray(vector<int>& arr) {
int n = arr.size();
if(n < 3) return false;
vector<int> p(n, 0), s(n, 0); // prefix & suffix
p[0] = s[n - 1] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) p[i] = arr[i] > arr[i - 1] && p[i - 1];
for(int i = n - 2; i >= 1; i--) s[i] = arr[i] > arr[i + 1] && s[i + 1];
for(int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) if(p[i] && s[i]) return true;
return false;
}
};
Approach 2: One Pass
From approach 1, we can see that both prefix and suffix array only record if it is a strictly increasing or decreasing array till certain point. We can optimise it using two pointers i and j, where pointer i is to check the strictly increasing array and pointer j is to check the strictly decreasing array. If they stop at the same point, then that would be the peak of the same mountain.
- C++
- Python
- JavaScript
class Solution {
public:
bool validMountainArray(vector<int>& arr) {
int n = arr.size(), i = 0, j = n - 1;
while (i + 1 < n && arr[i] < arr[i + 1]) i++;
while (j - 1 > 0 && arr[j - 1] > arr[j]) j--;
return i == j && i > 0 && j < n - 1;
}
};
class Solution:
def validMountainArray(self, arr: List[int]) -> bool:
l, r = 0, len(arr) - 1
if len(arr) < 3: return False
while l + 1 < len(arr) - 1 and arr[l] < arr[l + 1]:
l += 1
while r - 1 > 0 and arr[r] < arr[r - 1]:
r -= 1
return l == r
/**
* @param {number[]} arr
* @return {boolean}
*/
var validMountainArray = function (arr) {
let left = 0;
let right = arr.length - 1;
if (arr.length < 3) return false;
while (left + 1 < arr.length - 1 && arr[left] < arr[left + 1]) left++;
while (right - 1 > 0 && arr[right] < arr[right - 1]) right--;
return left == right;
};