2196 - Create Binary Tree From Descriptions (Medium)
Problem Link
https://leetcode.com/problems/create-binary-tree-from-descriptions/
Problem Statement
You are given a 2D integer array descriptions where descriptions[i] = [parent_i, child_i, isLeft_i] indicates that parent_i is the parent of child_i in a binary tree of unique values. Furthermore,
- If
isLeft_i == 1, thenchild_iis the left child ofparent_i. - If
isLeft_i == 0, thenchild_iis the right child ofparent_i.
Construct the binary tree described by descriptions and return its root.
The test cases will be generated such that the binary tree is valid.
Example 1:
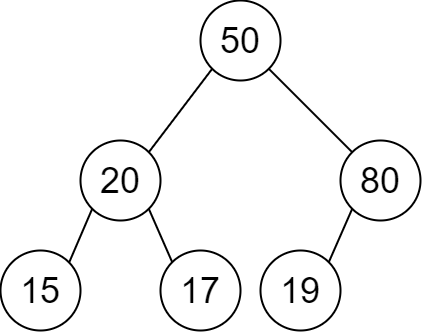
Input: descriptions = [[20,15,1],[20,17,0],[50,20,1],[50,80,0],[80,19,1]]
Output: [50,20,80,15,17,19]
Explanation: The root node is the node with value 50 since it has no parent.
The resulting binary tree is shown in the diagram.
Example 2:
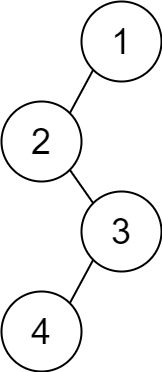
Input: descriptions = [[1,2,1],[2,3,0],[3,4,1]]
Output: [1,2,null,null,3,4]
Explanation: The root node is the node with value 1 since it has no parent.
The resulting binary tree is shown in the diagram.
Constraints:
1 <= descriptions.length <= 10^4descriptions[i].length == 31 <= parent_i, child_i <= 10^50 <= isLeft_i <= 1- The binary tree described by
descriptionsis valid.
Approach 1: Hash Map
We use a hash map to store the TreeNode* for the key and another hash map to store if this TreeNode* has a parent.
We iterate the input to get the values of parent, child and isLeft. Then we check if the parent and the child are in the hash map. If not, we create a new TreeNode for it and store it in hash map.
If is , that means the child is the left child of parent. Else, the child is the right child of parent.
At the end, we find out the node without parent, return that TreeNode because that is the root.
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* createBinaryTree(vector<vector<int>>& descriptions) {
unordered_map<int, TreeNode*> m;
unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> hasParent;
TreeNode* p = nullptr;
TreeNode* c = nullptr;
for (auto x : descriptions) {
int parent = x[0], child = x[1], isLeft = x[2];
// check if TreeNode* for parent is in hash map or not
if (m.count(parent)) {
// if so, store it in p
p = m[parent];
} else {
// if not, create a new one
p = new TreeNode(parent);
// and store it in hash map
m[parent] = p;
}
// check if TreeNode* for child is in hash map or not
if (m.count(child)) {
// if so, store it in c
c = m[child];
} else {
// if not, create a new one
c = new TreeNode(child);
// and store it in hash map
m[child] = c;
}
// if isLeft is 1, then this child is the left child of this parent
if (isLeft) p->left = c;
// else this child is the right child of this parent
else p->right = c;
// mark this child has a parent
hasParent[c] = 1;
}
// search for a TreeNode* without parent
for (auto x : m) {
// found -> return this TreeNode* as this is the root
if (!hasParent.count(x.second)) {
return m[x.first];
}
}
// never reach here
return nullptr;
}
};