0019 - Remove Nth Node From End of List (Easy)
Problem Link
https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
Problem Statement
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
Example 1:
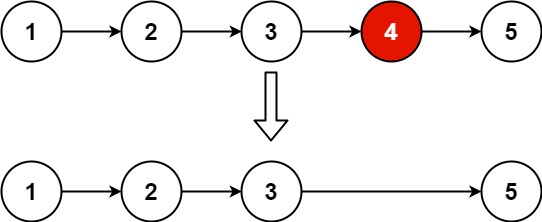
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output: [1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1, 2], n = 1
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
sz. 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
Follow up: Could you do this in one pass?
Approach 1: Fast and Slow Pointer
- C++
- Java
- Go
- Python
- JavaScript
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
// Time Complexity: O(N) where N is the number of nodes
// Space Complexity: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
// the general idea is to use fast & slow pointers
// 1. traverse L - n nodes from the start of the list using fast pointer
// where L is the length of the linked list
// e.g. in example 1, the fast pointer will be at node 3 while slower pointer remains at node 1
// 2. traverse slow pointer until fast pointer reaches the last node
// e.g. in example 1, the fast pointer will be at node 5 while slower pointer will be at node 3
// 3. update slow next node
// e.g. in example 1, the slower pointer is at node 3 now. we link the next node to node 5.
// therefore, we have 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 5 at the end
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
// move fast pointer to the n + 1 element
// now the distance between slow and fast pointer is n nodes
while (n--) fast = fast->next;
// if fast reached the end, we need to remove the first element
// e.g. head = [1], n = 1
if (fast == nullptr) return head->next;
// move both pointers at the same time until the fast pointer reaches the end
while (fast->next != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
// slow pointer will be pointing to the node before the one to be removed
// then we update the next node of the slow pointer
slow->next = slow->next->next;
return head;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
// Time Complexity: O(N) where N is the number of nodes
// Space Complexity: O(1)
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
// move fast pointer to the n + 1 element
// now the distance between slow and fast pointer is n nodes
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) fast = fast.next;
// if fast reached the end, we need to remove the first element
// e.g. head = [1], n = 1
if (fast == null) return head.next;
// move both pointers at the same time until
// the fast pointer reaches the end
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
// slow pointer will be pointing to the node before the one to be removed
// then we update the next node of the slow pointer
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return head;
}
}
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
// Time Complexity: O(N) where N is the number of nodes
// Space Complexity: O(1)
// the general idea is to use fast & slow pointers
// 1. traverse L - n nodes from the start of the list using fast pointer
// where L is the length of the linked list
// e.g. in example 1, the fast pointer will be at node 3 while slower pointer remains at node 1
// 2. traverse slow pointer until fast pointer reaches the last node
// e.g. in example 1, the fast pointer will be at node 5 while slower pointer will be at node 3
// 3. update slow next node
// e.g. in example 1, the slower pointer is at node 3 now. we link the next node to node 5.
// therefore, we have 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 5 at the end
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
slow := head
fast := head
// move fast pointer to the n + 1 element
// now the distance between slow and fast pointer is n nodes
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
fast = fast.Next
}
// if fast reached the end, we need to remove the first element
// e.g. head = [1], n = 1
if fast == nil {
return head.Next
}
// move both pointers at the same time until
// the fast pointer reaches the end
for fast.Next != nil {
fast = fast.Next
slow = slow.Next
}
// slow pointer will be pointing to the node before to one to be removed
// then we update the next node of the slow pointer
slow.Next = slow.Next.Next
return head
}
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
# Time Complexity: O(N) where N is the number of nodes
# Space Complexity: O(1)
class Solution:
# the general idea is to use fast & slow pointers
# 1. traverse L - n nodes from the start of the list using fast pointer
# where L is the length of the linked list
# e.g. in example 1, the fast pointer will be at node 3 while slower pointer remains at node 1
# 2. traverse slow pointer until fast pointer reaches the last node
# e.g. in example 1, the fast pointer will be at node 5 while slower pointer will be at node 3
# 3. update slow next node
# e.g. in example 1, the slower pointer is at node 3 now. we link the next node to node 5.
# therefore, we have 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 5 at the end
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
slow = fast = head
# move fast pointer to the n + 1 element
# now the distance between slow and fast pointer is n nodes
for i in range(n): fast = fast.next
# if fast reached the end, we need to remove the first element
# e.g. head = [1], n = 1
if fast is None: return head.next
# move both pointers at the same time until the fast pointer reaches the end
while fast.next:
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
# slow pointer will be pointing to the node before the one to be removed
# then we update the next node of the slow pointer
slow.next = slow.next.next
return head
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) {
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
fast = fast.next;
}
if (fast == null) {
return head.next;
}
while (fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return head;
};
Approach 2: Iteration with One Pass Solution
Decrement N and iterate fast and slow pointers, but only start slow pointer once N hit zero..
As stated in Example 1: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5, and n = 2
Size of the linked list is , and remove 2nd Node () from the last, so we need to stop at 3rd Node () from first when we iterate.
Iterate with fast pointer, till N becomes , fast pointer move to 3rd Node () then start with slow pointer.
Fast pointer is steps away to reach end (from the current 3rd Node ()). While we iterate till last node, fast pointer reach end at 5th node () and eventually slow pointer stops at 3rd Node (3), finally change the pointer to the next next node, that's it.
Time Complexity: , where - # of nodes in the list
Space complexity:
- Java
- Python
- JavaScript
- C++
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// Dummy head pointer to return head reference at the last
ListNode current = new ListNode();
current.next = head;
// Initialize slow and fast pointer to dummy head
ListNode slow = current, fast = current;
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
if (n <= 0) {
slow = slow.next;
}
n -= 1;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
// Head reference
return current.next;
}
}
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(next=head)
slow, fast = dummy, dummy
while fast.next:
fast = fast.next
if n <= 0:
slow = slow.next
n -= 1
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummy.next
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) {
let dummy = new ListNode();
dummy.next = head;
let slow = dummy,
fast = dummy;
while (fast.next) {
fast = fast.next;
if (n <= 0) {
slow = slow.next;
}
n--;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode();
dummy->next = head;
auto slow = dummy, fast = dummy;
while (fast->next) {
fast = fast->next;
if (n <= 0) {
slow = slow->next;
}
n--;
}
slow->next= slow->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};