0054 - Spiral Matrix (Medium)
Problem Link
https://leetcode.com/problems/spiral-matrix/
Problem Statement
Given an m x n matrix, return all elements of the matrix in spiral order.
Example 1:
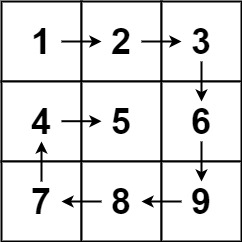
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
Example 2:

Input: matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]
Output: [1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
Approach 1: Spiral Order Search using Set.
We can just iterate the matrix in a spiral order, starting at the top left, and moving in the 4 cardinal directions, changing the direction if we ever hit a boundary or a previously visited cell.
This means we will need a few things, the order of our 4 directions, that is which is right, down, left, up. We will need an index to track where we are in our directions, and a visited set to prevent us from going to the same cell twice.
With all that set, we can just loop until our return array reaches the length of adding each cell to our array and visited set, and then checking our boundaries to make sure we move our position to the proper spot.
Time Complexity: where m is the number of rows, and n is the number of columns. We have to iterate each cell once in order to return the spiral order.
Space Complexity: , we need an array to return all the numbers in the matrix, and will also utilize a set to prevent revisiting cells.
- Python
class Solution:
def spiralOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
# INITILIZE the ROWS, COLS of matrix, the directions of
# spiral order, and an index to track which direction we are
# traversing.
ROWS, COLS = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
dirs = ((0,1), (1,0), (0,-1), (-1,0))
direction = 0
# initialize our return array, our visited set
spiral_order = []
visited = set()
# position in the matrix
r, c = 0, 0
while not len(spiral_order) == (ROWS * COLS):
# For our loop we will always just blindly add to the
# array and visited set, then check boundaries after.
spiral_order.append(matrix[r][c])
visited.add((r,c))
# check the next direction
dr, dc = dirs[direction]
nr, nc = dr + r, dc + c
# if next direction doesn't work.
if (nr >= ROWS or nr < 0 or
nc >= COLS or nc < 0 or
(nr, nc) in visited
):
# change direction
direction = direction + 1 if direction < len(dirs) - 1 else 0
# update the next cell using the direction we need to be
# travelling. Since we are using a visited, and boundary
# checking above, the new cell r,c will always point to an
# unvisited, inbounds cell.
dr, dc = dirs[direction]
r, c = r + dr, c + dc
return spiral_order