0138 - Copy List with Random Pointer (Medium)
Problem Link
https://leetcode.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/
Problem Statement
A linked list of length n is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or null.
Construct a deep copy of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly n brand new nodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list.
For example, if there are two nodes X and Y in the original list, where X.random --> Y, then for the corresponding two nodes x and y in the copied list, x.random --> y.
Return the head of the copied linked list.
The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representing Node.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) that therandompointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
Your code will only be given the head of the original linked list.
Example 1:
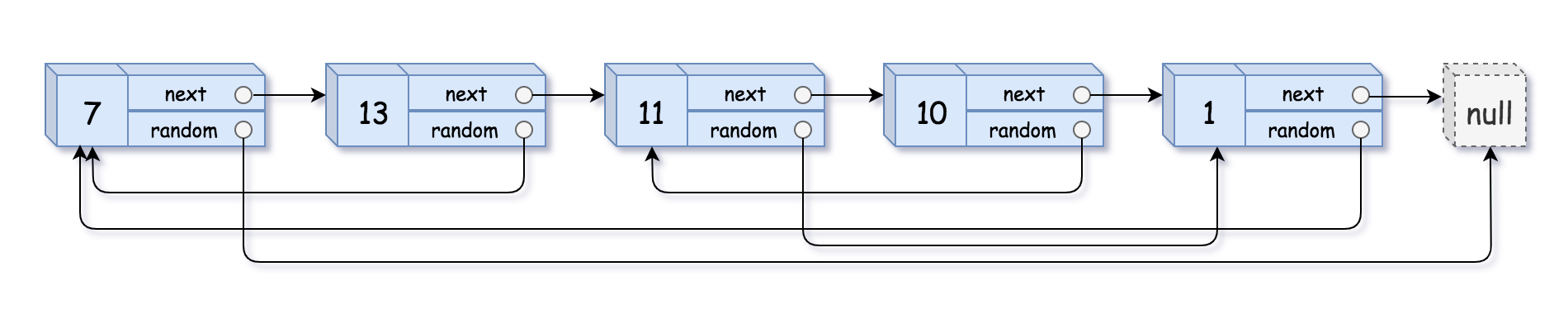
Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2:
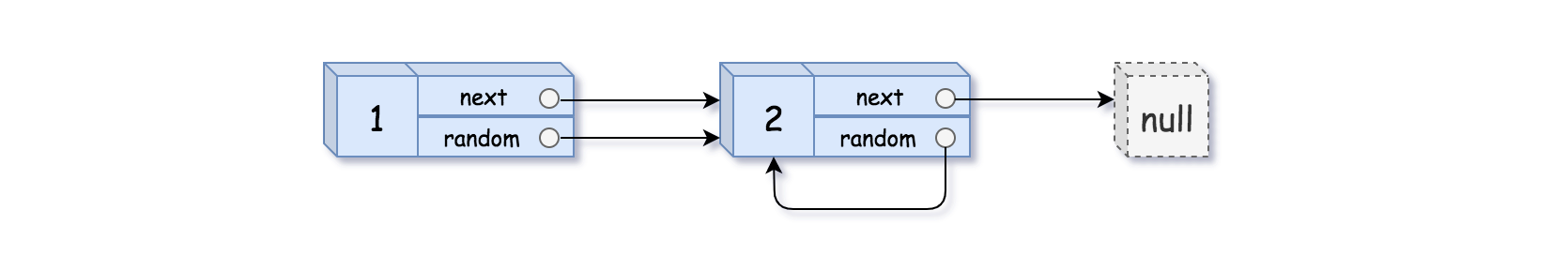
Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Example 3:
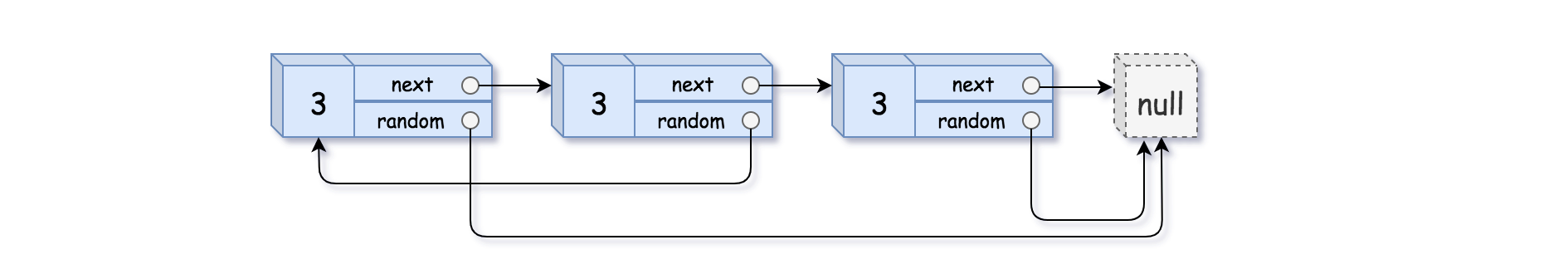
Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 1000-10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4Node.randomisnullor is pointing to some node in the linked list.
Approach 1: 2 Passes
We can break this problem down into 2 easy steps.
Step 1 is to loop through the linked list and make a copy of each node, we will place the nodes into a hash map with the original node as the key and the created node as the value. We do this for access later.
Step 2 is to loop through the linked list a second time, this time knowing that all the nodes have been created, we can access the nodes inside our hash map, and then set our pointers.
Time Complexity: we are going to do 2 passes through our linked list of size n.
Space Complexity: we need to create a hash map of size n, to map each node to.
- Python
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, x: int, next: 'Node' = None, random: 'Node' = None):
self.val = int(x)
self.next = next
self.random = random
"""
class Solution:
def copyRandomList(self, head: "Node") -> "Node":
# Base case, return early
if not head:
return head
# Hash map, default with None for when we reach a null node.
# {key:value} --> {original_node: copy_node}
original_to_copy = {None: None}
# node variable to loop through each node in the linked list
node = head
# while our node exists, ie. we haven't reached the end.
while node:
# create a copy node, using the original linked lists value
copy = Node(node.val)
# put the copied node into our hash map
original_to_copy[node] = copy
# move forward in our linked list
node = node.next
# node variable to loop through each node in the linked list
node = head
# while our node exists, ie. we haven't reached the end.
while node:
# get the copy, next and random nodes we created in the above loop.
copy = original_to_copy[node]
nxt = original_to_copy[node.next]
random = original_to_copy[node.random]
# set the next, and random for our copied node to proper nodes.
copy.next, copy.random = nxt, random
# more vorward in our linked list
node = node.next
# return head of our linked list. Since it exists in hash map, we can
# retrieve it using the original head as the key.
return original_to_copy[head]
Approach 2: Single Pass
Now a slightly trickier approach, is it possible to do the above in a single pass? Of course. To do that though, we are going to have to be careful to make sure we are reusing any node that has already been created, and creating nodes that don't exist. That can simply be done though by using a hash map again for access to see if the node exists, and then creating the node if it doesn't exist.
We can do all this, by making sure at each iteration of our loop through the list that all nodes exists and then setting the pointers.
To do that, we check if the node as been created before, if not create it and put it in the hash map, with the key as the original node, and the value as the created node. Note that we are looping only through valid nodes, so while for our current node we don't need to check if it is a null node, we will have to handle null node cases for our next and random nodes.
Time Complexity: we are going to do a single pass through all nodes in the linked list.
Space Complexity: we need to create a hash map of size n, to map each node to.
- Python
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, x: int, next: 'Node' = None, random: 'Node' = None):
self.val = int(x)
self.next = next
self.random = random
"""
class Solution:
def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':
# Base case, given empty head
if not head:
return head
# Create our hash map for O(1) access
# {key:value} --> {original_node: copy_node}
original_to_copy = {}
# Set a node variable to loop through all the nodes in linked list.
node = head
while node:
#Get/Create current node.
if node in original_to_copy:
# Node exists, get the node
n = original_to_copy[node]
else:
# node doesn't exist, create it, add to the hash map.
n = Node(node.val)
original_to_copy[node] = n
#Get/Create node.next. Default it to None to handle the case in which
# the node actually is a null node.
nxt = None
if node.next in original_to_copy:
# Next copy exists, get the node
nxt = original_to_copy[node.next]
elif node.next:
# next copy doesn't exist, create it and add it to the hash map.
nxt = Node(node.next.val)
original_to_copy[node.next] = nxt
#Get/Create node.random. Default it to None to handle the case in which
# the node actually is a null node.
rand = None
if node.random in original_to_copy:
# random copy exists, get the node.
rand = original_to_copy[node.random]
elif node.random:
# random copy doesn't exist, create it and add it to the hash map.
rand = Node(node.random.val)
original_to_copy[node.random] = rand
# Got/Created all our nodes, now set the pointers
n.next = nxt
n.random = rand
# move our pointer up.
node = node.next
# return head of our linked list. Since it exists in the hash map, we can
# retrieve it using the original head as the key.
return original_to_copy[head]