0148 - Sort List (Medium)
Problem Link
https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-list/
Problem Statement
Given the head of a linked list, return the list after sorting it in ascending order.
Example 1:
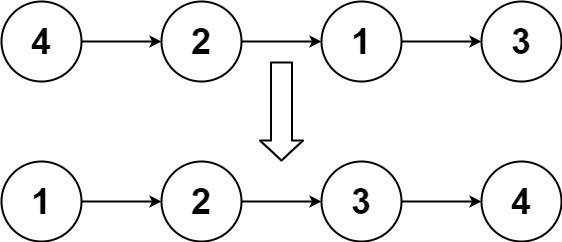
Input: head = [4,2,1,3]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Example 2:

Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 5 * 10^4]. -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Follow up: Can you sort the linked list in O(n logn) time and O(1) memory (i.e. constant space)?
Approach 1: Recursive Merge Sort
- Find the middle node and cut the head reference till middle node
- Keep reducing the nodes size to smaller for comparison (same as like merge sort)
- Once we reduce nodes size to 1, merge the nodes in sorted (ascending) order.
- Keep merging the nodes till last, to build the sorted list.
Time Complexity: , where - # of nodes in the list
Space complexity: , - recursive call stack
- Java
- Python
- JavaScript
- C++
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (Objects.isNull(head) || Objects.isNull(head.next)) {
return head;
}
// Middle node
ListNode mid = middleNode(head);
// Keep traversing left to get the smallest nodes for comparison (smallest we can get is 1 node)
ListNode left = sortList(head);
// Starting from middle, to find the smallest nodes for comparison
ListNode right = sortList(mid);
// Compare the list and return the merged nodes
return mergeTwoLists(left, right);
}
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode midPrev = null;
//
while (head != null && head.next != null) {
midPrev = (midPrev == null) ? head : midPrev.next;
head = head.next.next;
}
ListNode mid = midPrev.next;
// Cut the reference to the next pointer (mid), so that head remains from start to mid.
midPrev.next = null;
return mid;
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// Base case
if (Objects.isNull(list1) && Objects.isNull(list2)) {
return list1;
}
if (Objects.isNull(list1)) {
return list2;
}
if (Objects.isNull(list2)) {
return list1;
}
ListNode head = new ListNode();
ListNode node = head;
while (Objects.nonNull(list1) && Objects.nonNull(list2)) {
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
node.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
node.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
node = node.next;
}
// If either of half is not empty then append it
node.next = Objects.nonNull(list1) ? list1 : list2;
return head.next;
}
}
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head):
# Base case
if not head or not head.next:
return head
# split the list into two halfs
slow, fast = head, head.next
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
start = slow.next
slow.next = None
# Sort left portion
left = self.sortList(head)
# Sort right portion
right = self.sortList(start)
# Merge them and return
return self.merge(left, right)
def merge(self, list1, list2):
tail = dummy = ListNode()
# while list1 and list2 are not empty
while list1 and list2:
# Find smaller value
if list1.val < list2.val:
tail.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
else:
tail.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
tail = tail.next
# it's possible that one of two lists are not empty
if list1:
tail.next = list1
if list2:
tail.next = list2
return dummy.next
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var sortList = function (head) {
// base case
if (!head || !head.next) return head;
// split the list into two halfs
// two pointers
let slow = head;
let fast = head.next;
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
let start = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
// sort left portion
let left = sortList(head);
// sort right portion
let right = sortList(start);
// merge them and return
return merge(left, right);
};
// merge sort function
function merge(list1, list2) {
let tail = (dummy = new ListNode());
// while list1 and list2 are not empty
while (list1 && list2) {
// find smaller value
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
tail.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
tail.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
// it's possible that one of two lists are not empty
if (list1) tail.next = list1;
if (list2) tail.next = list2;
return dummy.next;
}
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
// base case
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
// split list into two halfs
// slow and fast pointer
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head->next;
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
ListNode* start = slow->next;
slow->next = NULL;
// sort left portion
ListNode* left = sortList(head);
// sort right portion
ListNode* right = sortList(start);
// merge left and right portion
return merge(left, right);
}
// merge sort function
ListNode* merge(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* tail = dummy;
// while both lists are not empty
while (list1 && list2) {
// find smaller value
if (list1->val < list2->val) {
tail->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
} else {
tail->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
// it's possible that one of two lists are not empty
if (list1) tail->next = list1;
if (list2) tail->next = list2;
return dummy->next;
}
};